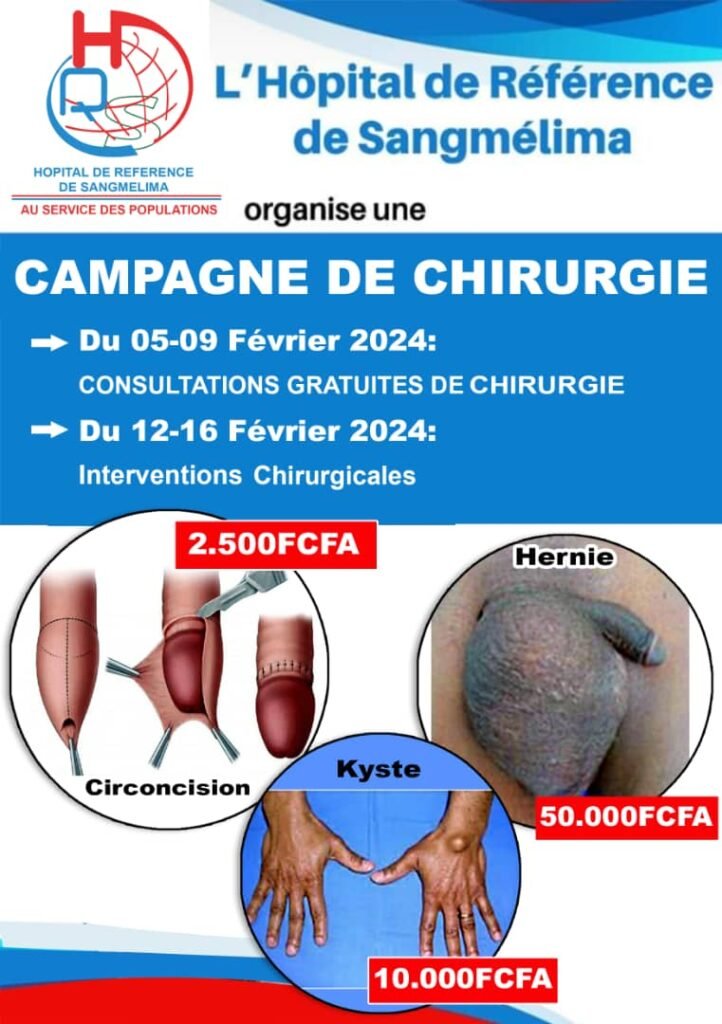
Chicory : It ensures a depuration of the liver

It stimulates the intestinal flora, which, once regulated, will protect against infections and stimulate the proper functioning of the immune system.
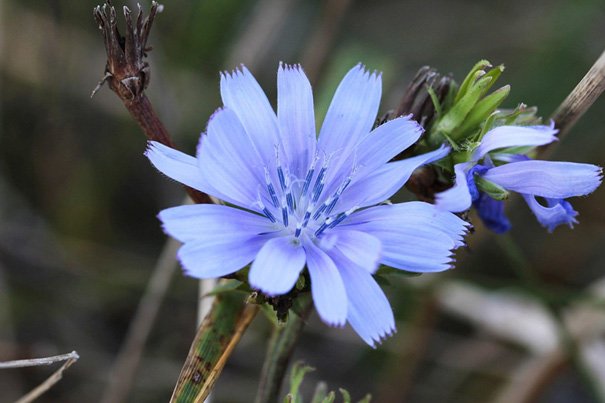
Used for thousands of years for its medicinal properties, chicory is better known today as a substitute for coffee, yet its many benefits justify a closer look at this plant. Bitter chicory (Cichorium intybus) is a wild herbaceous plant with a conical taproot that is widely used in phytotherapy. It grows spontaneously in ditches, meadows and wastelands in Europe, Asia and North Africa and can grow up to 1 m high. This plant has azure-blue flowers from May to September and belongs to the Asteraceae family. A coffee substitute, food colouring and natural flavouring,
bitter chicory is grown for industrial purposes, particularly in northern France where its root is harvested in September, dried and then roasted to powder. This coffee substitute is very interesting because its taste is close to that of coffee, without the addition
of caffeine, so it can also be consumed in the evening, as well as by pregnant women or people prone to high blood pressure.
Bitter chicory should not be confused with its cultivated chicory cousins, which are derived from it, and which therefore belong to the same botanical
genus, or even the same species: endive and curly endive (Cichorium endivia); other varieties
of the Cichorium intybus species: red chicory (treviso), green chicory (sugarloaf); endive or chicory (witloof) is also part of the same Cichorium intybus species. Finally, the capuchin beard is the regrowth of the wild chicory root, forced like endives, in autumn. This low-calorie plant is rich in minerals (phosphorus, magnesium, iron) and is also full of vitamins (A, C, B9, K and E). It is an excellent source of fibre and helps with intestinal transit. Used for thousands of years, bitter chicory is an indispensable plant in traditional medicine. Ideal for calming digestive disorders, it is a tonic and an aperitif. Antioxidants The inulin present in the plant is a prebiotic: it stimulates the intestinal flora, which, once regulated, will protect against infections and stimulate the proper functioning of the immune system. Inulin also limits blood sugar levels and ensures better absorption of iron, calcium and magnesium. Bitter chicory is full of antioxidants that fight against cell ageing. Cholagogue, chicory also allows a better elimination
of bile. It also cleanses the liver and is a good diuretic. Like other bitter plants, but also milk thistle, artichoke or black radish, it facilitates hepatic drainage. It can therefore be used as part of a detoxification cure. Externally, the leaves are used as poultices to relieve dry skin, irritations and inflammations